What Is a Swollen Eyelid?
Eyelid swelling occurs when the area around your eyes fills up with fluid, making them appear puffy. Eyelid edema is the medical term for fluid retention in the eyelid.
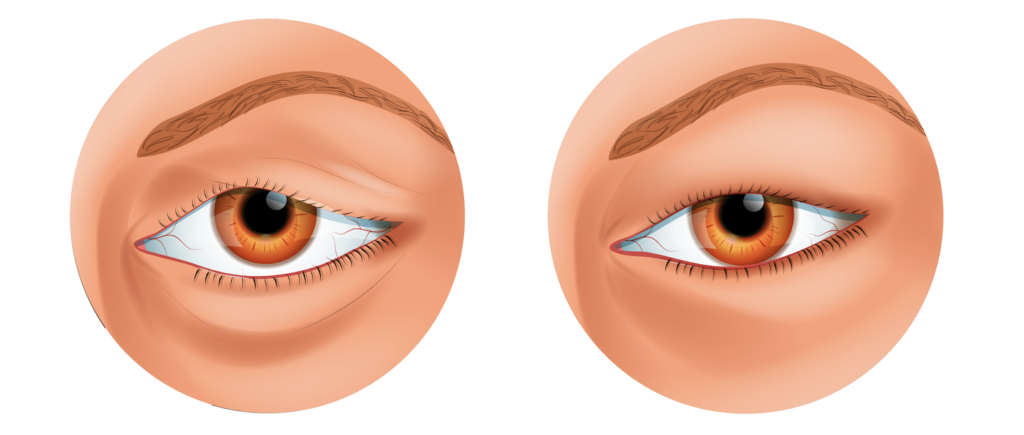
Swollen eyelids can result from a lack of sleep or may be a sign of a medical condition. Infections, trauma, and eye diseases can lead to swelling in the eyelid.
Eyelid swelling can occur in one or both eyes. You may also experience pain, itching, or eye irritation.
Keep reading to learn about common causes of swollen eyelids, including potential treatments and when to see a doctor.
When to See a Doctor
If your eyelid remains swollen for more than 48 hours, seek immediate medical attention.
Eyelid swelling with certain symptoms may indicate a more serious underlying condition. Contact your healthcare provider right away if you experience:
- Sudden vision loss
- Painful eye movements
- Swelling after head trauma
- Anaphylaxis symptoms such as swelling of the tongue, lips, and mouth
- Bulging eyes
- Severe headache
- Stiff neck
- Severe fever (higher than 101 degrees Fahrenheit)
A physician or eye doctor will diagnose your condition and prepare you for treatment. If the reason for the swollen eyelid is severe enough, they may refer you to an ophthalmologist.
12 Causes of Swollen Eyelids
There are many reasons why your eyelids may be swollen. Eyelid swelling is often a sign of another medical condition, such as:
1. Eye Allergies
Allergic reactions trigger a histamine release in your body, which causes redness, itching, and swelling. Because the eyelid skin is so sensitive, an allergic reaction can lead to severe inflammation.
Common causes of eye allergies include:
- Seasonal allergies (hay fever)
- Chemicals in personal care products and makeup
- Dust
- Pet dander
- Smoke
- Perfumes
- Foods
Symptoms
Common eye allergy symptoms include:
- Pink or red eyes
- Eye pain in one or both eyes
- Puffy eyelid
- Itchiness in the eyes
- A burning sensation in the eyes
- Teary eyes
- Sensitivity to light
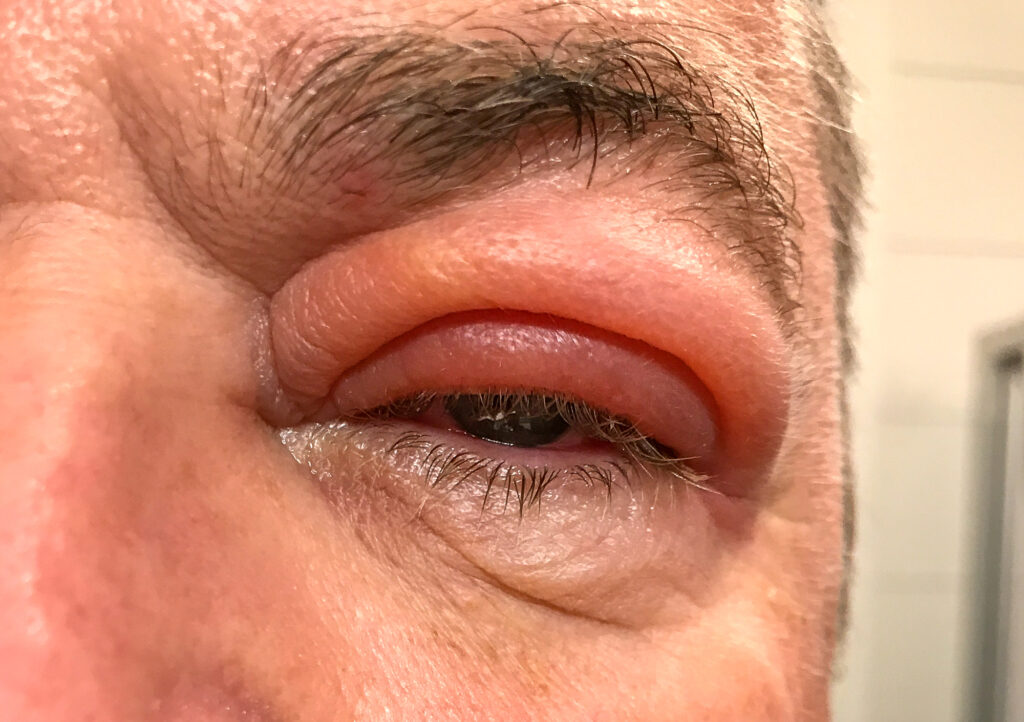
Treatment
Treatment options for eye allergies include:
- Cool compresses. To reduce swelling and relieve itching
- Antihistamines. Such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
- Artificial tears. To soothe itching and dryness
- Prescription medications. Oral allergy medicine or eye drops
2. Conjunctivitis (Pink Eye)
Conjunctivitis is inflammation of the conjunctiva — the thin tissue that lines your eyelids and the white of your eye. The condition can affect one or both eyes.
Potential causes include:
- Adenovirus infection
- Bacterial infection
- Allergic reaction
Symptoms
A swollen eyelid is a common symptom of pink eye. Other symptoms include:
- Pink or red eyeball
- Itching
- Pain or discomfort
- Eye discharge
Treatment
Infectious viral conjunctivitis is very contagious and requires professional medical attention.
Depending on the cause, conjunctivitis treatment may include:
- Cool compress
- Artificial tears
- Antibiotics
- Antiviral therapy
- Antihistamines
3. Ocular Herpes
Eye herpes, sometimes termed ocular herpes, may produce painful sores on the eyelid or the eye surface. Both the cornea and the eyelid may be affected.
Symptoms
Symptoms of ocular herpes include:
- Eyelids stuck together with mucus in the morning
- Swollen eyelids
- Red, itchy, and irritated eyelids
- Painful sores on the eyelid or surface of the eye
Treatment
Ocular herpes requires professional medical treatment, which may include:
- Prescription eye drops containing steroids, antibiotics, or both
- Antiviral medications
- Lubricating eye drops to alleviate dry eye
4. Cellulitis
Cellulitis causes severe swelling and calls for emergency medical care.
Two major kinds of cellulitis cause eyelid swelling:
- Orbital cellulitis. It is linked to a sinus infection that spreads to the tissues behind the eye
- Preseptal cellulitis, also called periorbital cellulitis. An infection of the eyelid skin
Symptoms
People suffering from orbital cellulitis may experience a bulging eye and pain while shifting their eyes back and forth.
Other symptoms include:
- Eyelid swelling
- Redness
- Pain
- Double vision
- Blurry vision
Treatment
Treatment includes antibiotic therapy targeting the bacteria. Symptoms often improve within 24 to 48 hours.
5. Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is a thyroid problem that can cause the eyelids to swell or bulge out of the sockets.
According to research, hyperthyroidism (high levels of thyroid hormones) can cause the eyes to swell or seem puffy.4 This is because the condition affects muscles and tissues around the eye.
Symptoms
Symptoms include:
- Eyes bulging from the eye socket
- Red, irritated eyes
- Double vision or reduced vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Gritty sensation in the eyes
- Pressure or pain in the eyes
Treatment
Treatment options include:
- Artificial tears or eye drops
- Oral steroids
- FDA-approved Tepezza, which reduces eye protrusion5
- Radiation therapy
- Orbital decompression surgery to fix bulging eyes
6. Chalazion
A chalazion is a small lump on the inner rim of the upper or lower eyelid. It’s usually painless but can cause redness and swelling.
People with the skin condition rosacea have a higher risk of developing chalazia.
Symptoms
Additional symptoms include:
- Swelling that may affect the entire eyelid
- Redness
- Blurry vision
- A hard lump on the eyelid
Treatment
Most cases of chalazia are treated at home. You can do the following:
- Apply a wet washcloth to the eye several times a day
- Practice good hygiene in the affected area
- Gentle eyelid massage
Call your doctor if the bump doesn’t go away after a few days or if there are signs of infection, such as fever.
7. Stye
A stye or hordeolum is a sensitive red lump caused by inflammation of the eyelash follicles. It looks and feels like a small pimple. Without treatment, a stye can develop into a chalazion.
Symptoms
Symptoms of a stye include:
- Swelling and redness
- Eye crusting and discharge
- Scratchy sensation
- A painful pimple-like lump that feels better once it drains
Treatment
Treatment options include:
- Warm compress
- Gentle eyelid massage
- Eye drops and other antibiotic ointments
Consult your healthcare professional if your stye lasts longer than a week despite home remedies.
8. Blepharitis
Blepharitis is eyelid inflammation. Blepharitis causes the eyelid margins to swell, flake, and scale. It’s caused by an overgrowth of bacteria usually present on the eyelids.
According to the National Eye Institute, there are two types of blepharitis:9
- Anterior blepharitis. Affects the exterior eyelid where eyelashes attach
- Posterior blepharitis. Affects the inner edge of the eyelid, including the oil glands
Symptoms
Blepharitis symptoms include:
- Crusted eyelid margins
- Dry eyes
- Loss of eyelashes
- Watery eyes
- Itchy and gritty feeling in the eyes
- Eye discharge
- Red or sore eyes
- A build-up of eyelid debris
- Blurred vision
Treatment
It’s essential to keep the eyelids clean during a blepharitis flareup.
Treatment options include:
- Warm compresses
- Washing the eyelid with a cotton swab soaked in water and diluted baby shampoo
- Gentle eyelid massage
- Topical steroids
- Topical antibiotics
- Eyelid scrubs
- Pulsation therapy to remove debris from oil glands
9. Eye Trauma
Skull fractures, burns, direct impact, foreign objects in the eye, and surgery may cause eyelid swelling.
A qualified healthcare professional should always examine eye injury to rule out any potential dangers.
Symptoms
People with an eye injury may experience:
- Pain and swelling of the eye
- Loss of vision
- Cut, torn, or inflamed eyelids
- Unusual pupil shape
- Reddening of the eyes
- A gritty feeling in the eyes
Treatment
Treatment depends on the type of injury and may include:
- Gentle cold compress
- Eye flushing to remove any chemicals or irritants
- Eye drops to help with healing
- An eye patch to cover the eye while it’s healing
10. Fatigue
Lack of sleep is a common cause of swollen eyelids and bags under the eyes. Fatigue is the likely culprit if you wake up with puffy eyes after a poor night’s sleep.
Symptoms
Other symptoms of fatigue include difficulty concentrating, irritability, and headaches.
Treatment
Applying a cold compress can alleviate eyelid swelling due to fatigue. However, a better solution is to prevent fatigue by getting enough sleep. Most people need 7 to 9 hours a night.
11. Fluid Retention
Eyelid edema is fluid retention around the eyes. It can be a sign of an underlying health condition, such as:
- Heart failure
- Lymphedema
- Thyroid problems
- Liver or kidney disease
- Obstructive sleep apnea
Symptoms and treatment of fluid retention vary based on the underlying cause.
12. Eye Cancer
Although rare, eye cancer is associated with swelling of the eyelids. Eye cancer is an abnormal growth of cells in the eyes, resulting in a tumor.
Many types of cancer can affect the eyes, including lymphoma, melanoma, and squamous cell carcinoma.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye cancer may include:
- Blurred vision
- Swollen eyelids
- Bulging of the affected eye
- Partial or total loss of vision
- Persistent eye irritation
- A lump on the eyelid or in the eye that grows larger
- Floaters, shadows, or flashes of light
- Pain in or around the eye (rare)
Treatment
Treatment options include:
- Radiotherapy
- Chemotherapy
- Surgical removal of the tumor
Treatment Options for Swollen Eyelids
You can treat most cases of eyelid swelling at home with easy home treatments such as cold compresses. Medical treatment may be necessary in some cases.
Home Remedies
Common home remedies for swollen eyelids include:
- Gently clean the eyelid skin using water and baby shampoo, then pat the area dry
- Use artificial tears to rinse and lubricate dry eyes
- Apply a cool compress or cold pack
- Use a cotton swab or clean fingertip to apply a gentle massage
- Rest with your head elevated to drain fluids away from the eyes
- Avoid wearing contact lenses until your swollen eyelids fully recover
Medical Treatments
Common medical treatments for swollen eyelids include:
- Allergy treatments. Allergy shots and prescription medicines
- Antibiotic eye drops. For bacterial infections
- Antiviral eye drops. For viral eye infections such as herpes
- Corticosteroids. To ease inflammation
- Incision and drainage. Of styes and chalazia
- Epinephrine injection. In cases of anaphylaxis
- Surgery. To remove foreign objects, tumors, or growths
How to Prevent Eyelid Swelling
It’s not always possible to prevent a swollen eyelid. However, you may be able to reduce your risk by taking the following steps:
- Treat your allergies
- Wash your hands with soap and warm water before touching your eyes
- Use hypoallergenic makeup and skin care products
- See your eye doctor for regular checkups
- Handle your contact lenses with care
Outlook
Eyelid swelling usually goes away within 24 to 48 hours. However, if an underlying condition causes the swelling, treatment may be required to address that condition.
Summary
Many things can cause a swollen eyelid, including lack of sleep, eye diseases, and trauma. Swelling that’s severe or lasts more than two days may be a sign of a medical condition that needs treatment.
Seek emergency medical attention if you experience eyelid swelling, sudden vision changes, high fever, or pain when moving your eye.
Don’t hesitate to call your healthcare provider if you’re unsure whether eyelid swelling is a cause for concern.
In this article